
Metal-Management Company manufactures and installs technological equipment for building and reconstruction of municipal wastewater treatment plants including accessories (screens, inflow baskets, check gates, filters, equipment for machine extraction of gravel and sand etc.) and project, shop and assembly drawings processing.
Technology of wastewater treatment
Function of biological treatment of Stainless Cleaner WWTPs is based on activation principle using fine bubble aeration. The activation is designed as low-charge system with high value of sludge age and aerobic stabilization of the sludge.
Advantages of WWTPs Stainless Cleaner
-
wide range of application
-
high efficiency of treatment
Reached quality of treated wastewaters enables their discharging into receiving stream without problems.
-
flexible operation
Material and hydraulic load of WWTP can vary in range of 30 to 120 % of capacity. WWTP can be possibly operated in sequent connecting of several resources of wastewater. Design with two technological reactors allows operating WWTP when load is variable. When first technological reactor is disturbed, then wastewater will be treated on second technological reactor for necessary period. That way will not let untreated wastewaters discharging into receiving stream.
-
silent operation without unpleasant odour
-
low operating costs
WWTP is constructed as a compact unit and the compact unit reduces hydraulic losses and consumption of electric energy.
-
reduced excess sludge formation and its next use
Sludge is aerobically stabilized, good flexible, further it doesn’t decompose and it doesn’t cause sensory faults. The sludge is without harmful substances; it could be used as a compost component.
-
simple service and maintenance
-
safety of operation
-
low requirements on needed space, optimal location
Biological reactor is constructed as a compact unit, which is divided by partitions to functional areas, which are mutually connected into circulation circuit. Reduced dimensions of the reactor enable roofing.
-
simple and fast training of operating personnel
Control of the operation can be optimized by following simple instructions of the operating manual. This leads to minimal maintenance and easy operation of the unit.
-
possibility of reconstruction of existing septics or basins
Existing septic (if septic is watertight) could be reconstructed as tank for technological built-in parts of WWTP.
-
possibility of reconstruction and intensification of existing WWTPs
Simplicity of technology and very good results of water treatment make possible that the existing WWTPs can be reconstructed and their operation intensified from the economic and environmental point of view.
Particular stages of wastewater treatment - single line technology
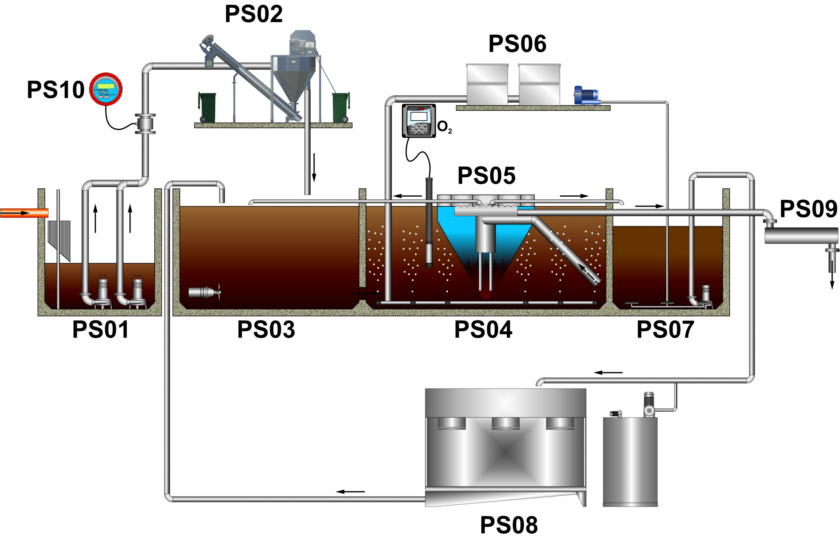 |
| Flow diagram of WWTP Stainless Cleaner - single line technology |
-
PS01 - pumping station with inflow basket
-
PS02 - fine mechanical pretreatment
-
PS03 - biological treatment - denitrification
-
PS04 - biological treatment - aeration-nitrification
-
PS05 - biological treatment - clarifier
-
PS06 - blower room
-
PS07 - sludge management - aerobical sludge digestion
-
PS08 - sludge management - sludge dewatering
-
PS09 - tertiary treatment - disinfection
-
PS10 - measuring and control
Particular stages of wastewater treatment - double line technology
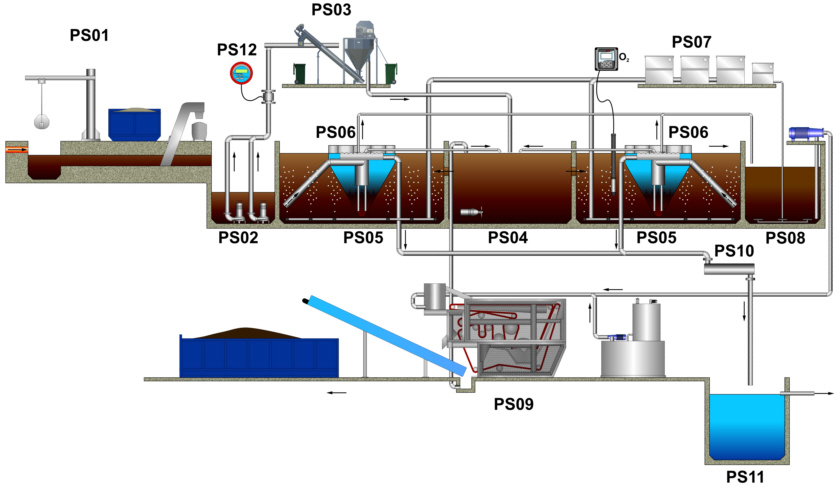 |
| Flow diagram of WWTP Stainless Cleaner - double line technology |
-
PS01 - coarse mechanical pre-treatment
-
PS02 - pumping station
-
PS03 - fine mechanical pre-treatment
-
PS04 - biological treatment - denitrifiction
-
PS05 - biological treatment - aeration-nitrification
-
PS06 - biological treatment - clarifier
-
PS07 - blower room
-
PS08 - sludge management - aerobical sludge digestion
-
PS09 - sludge management - sludge dewatering
-
PS10 - tertiary treatment - desinfection
-
PS11 - usage of final effluent for operation purposes
-
PS12 - measuring and control

