
Application
Equipment is designed for extraction of gravel and sand, which is caught in gravel catcher using travel with pulley blocks and a grab. The equipment is produced in version with stationary or rotating supporting structure and with volume of grab 50 l or 100 l. The grab has electromechanical drive (both electric lifting and travel). Advantage of modern electromechanical drive of the grab (solved via two electric pulley blocks), comparing with hydraulic systems, is the fact that you can extract with it gravel and sand from any depth and there are no problems with hydraulic fluid during winter period. Also there is no risk of endangering environment when hoses are damaged and the hydraulic fluid leaks into wastewater.
Technical description
The equipment consists of:
- supporting structure (stationary or rotary)
- travel with pulley blocks,
- grab
- electric switchboard
Equipment with stationary supporting structure STS-S
Stationary supporting structure is welded from rolled profiles. Length of one supporting span can be up to 6 m. Travel I-beam is fixed on columns, which are fixed in concrete foots. On the first column, there is placed footbridge for check and maintenance of travel with pulley blocks. Above the footbridge there is small roof, under which the travel with pulley blocks and grab must be placed during period, when the equipment is not used. The equipment is produced in version with one (travel length up to 6 m), two (travel length up to 12 m) or three (travel length up to 18 m) supporting spans. The supporting construction can be adapted to the customer's needs with respect to static and dynamic load capacity.
  |
| Plant for Machine Extraction of Gravel and Sand at WWTP Troubky |
Equipment with stationary supporting structure is produced with grab volume either 50 l and lifting capacity of pulley blocks 250 kg (type STS-S 250/50) or with grab volume 100 l and lifting capacity of pulley blocks 1000 kg (type STS-S 1000/100). Supporting structure and the grab are hot galvanized.
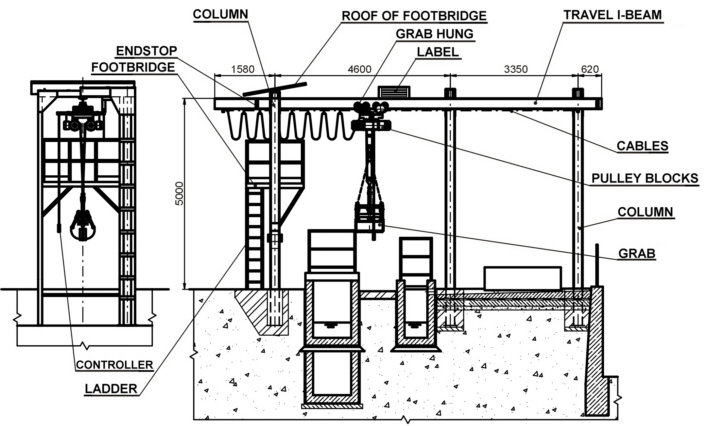 |
| Drawing of STS-S |
Equipment with rotating supporting structure STS-R (with manually rotating gib) and STS-RE (with electrically rotating gib)
Rotating supporting structure is made as stationary column fixed into concrete foot with rotating gib. Manually rotating arrangement requires from the operator, except lift and travel control, also manual rotation of gib. The plant can be optinally equipped with electrically rotating gib (power input for gib rotation drive is 120 W / 400 V). Gib rotation range is 250°.
  |
| Plant for Machine Extraction of Gravel and Sand with manually rotating gib at WWTP Jilove near Prague |
  |
| Plant for Machine Extraction of Gravel and Sand with electrically rotating gib at WWTP Rychvald |
Equipment with rotating supporting structure is produced with grab volume 50 l and lifting capacity of pulley blocks 250 kg (type designation STS-R 250/50 for the version with manually rotating gib and STS-RE 250/50 for the version with electrically rotating gib). Supporting structure and grab are hot galvanized.
Before the installation it is necessary to prepare concrete foot (standard dimensions of foot are 1600 x 1600 x 1000 mm, but its size must be assessed according to bearing capacity of the terrain), flange which will be put in concrete foot and on which will be fixed the column is included in delivery. It is necessary to bring electric cable CYKY 5Cx4, protection 20 A at installation place.
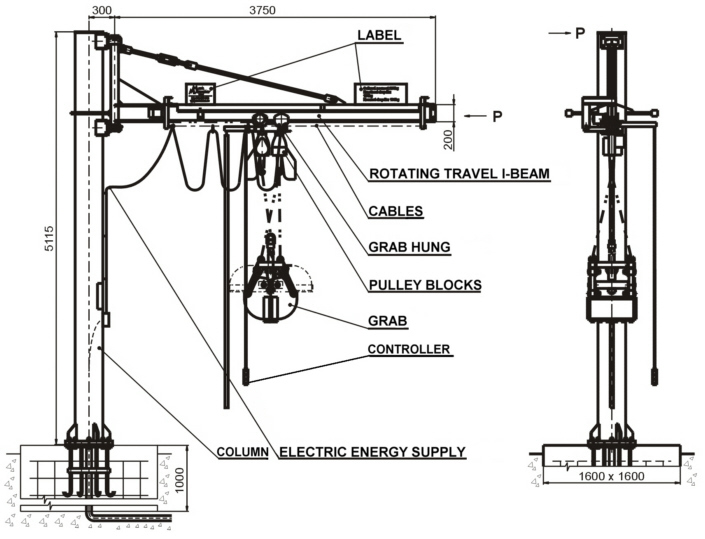 |
| Drawing of STS-R 250/50 |
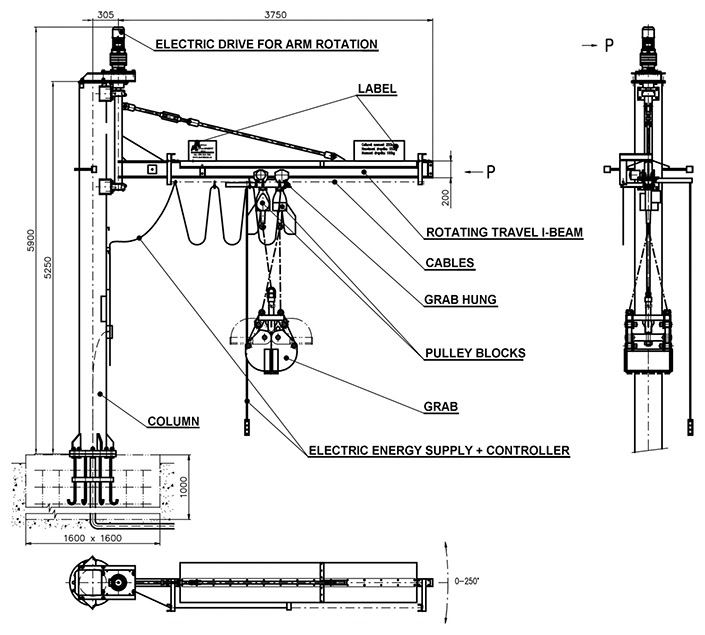 |
| Drawing of STS-RE 250/50 |
Travel with pulley blocks
For travel, lifting, lowering, opening and closing the grab are used two electric pulley blocks, which are fixed on travel. Travelling and lifting have electric drive. All movements are controlled from four-button controller, which hangs on cable and wire (at STS-RE there is a six-button controller).
| Volume of grab | Lifting capacity of pulley blocks | Travel power input | Lifting power input |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 l | 250 kg | 250 W / 400 V | 2 x 360 W / 400 V |
| 100 l | 1000 kg | 2 x 250 W / 400 V | 2 x 1,45 kW / 400 V |
Grab
Grab with volume 50 l or 100 l is hung at electric pulley bloc. It is made as double-chain with gradual opening and closing of jaws. Opening and closing is made via second electric pulley block.
Electric installation
Electric pulley blocks are connected to tension 3 x 400 V through inlet cable, which hangs on cable riders, this cable is then led on column to height circa 1,5 m over the ground, where is connected into electric switchboard. Main switch is lockable.
Selected references
| Place of installation | Type | Year of installation |
|---|---|---|
| WWTP Kraslice | STS-S 1000/100 | 1999 |
| WWTP Troubky | STS-S 1000/100 | 2002 |
| WWTP Dobruska | STS-S 1000/100 | 2002 |
| WWTP Kostelec nad Orlici | STS-S 1000/100 | 2002 |
| WWTP Police nad Metuji | STS-S 1000/100 | 2002 |
| WWTP Jilove | STS-R 250/50 | 2003 |
| WWTP Morkovice | STS-S 500/50(without supporting structure) | 2003 |
| WWTP Revnice | STS-R 250/50 | 2003 |
| WWTP Sobotka | STS-S 250/50 | 2004 |
| WWTP Vestec | STS-R 250/50 | 2005 |
| WWTP Zacler | STS-R 250/50 | 2005 |
| WWTP Vrbno pod Pradedem | STS-R 250/50 | 2005 |
| WWTP Budisov nad Budisovkou | STS-S 250/50 | 2005 |
| WWTP Solnice | STS-S 1000/100(without supporting structure) | 2007 |
| WWTP Opava | STS-S 1000/100(without supporting structure) | 2007 |
| WWTP Podborany | STS-R 250/50 | 2008 |
| WWTP Marianske udoli | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2008 |
| WWTP Lazne Belohrad | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2008 |
| WWTP Sternberk | STS-R 250/50 | 2009 |
| WWTP Cesky Tesin | STS-S 1000/100(without supporting structure) | 2009 |
| WWTP Ujezd u Brna | STS-R 250/50 | 2009 |
| WWTP Mlada Vozice | STS-R 250/50 | 2009 |
| WWTP Slušovice | STS-R 250/50 | 2010 |
| WWTP Rudna | STS-R 250/50 | 2010 |
| WWTP Jince | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2010 |
| WWTP Opocno-Vodetin | STS-R 250/50 | 2011 |
| WWTP Bila Tremesna | STS-R 250/50 | 2011 |
| WWTP Koberice | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2012 |
| WWTP Destne in Orlicke hory | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2012 |
| WWTP Havirov | STS-S 1000/130(without supporting structure) | 2012 |
| WWTP Nevsova | STS-S 250/50 | 2012 |
| WWTP Zlechov | STS-S 250/50(without supporting structure) | 2012 |
| WWTP Trinec | STS-S 1000/100(without supporting structure) | 2012 |
| WWTP Vilemov | STS-R 250/50 | 2013 |
| WWTP Zlate Hory | STS-R 250/50 | 2013 |
| WWTP Chlebicov | STS-R 250/50 | 2013 |
| WWTP Vilemov 2 | STS-S 250/50 (without supporting structure) | 2013 |
| WWTP Rychvald | STS-RE 250/50 | 2014 |

